From BCBS 239 to RDARR – What banks need to implement now
With RDARR, BaFin and the ECB are tightening the requirements for risk data and data governance. Interpretable principles are becoming verifiable standards – with a focus on data quality, responsibilities and IT architectures. Read about what has changed compared to BCBS 239 and how banks can now implement the new requirements in a structured and audit-proof manner.

BCBS 239, officially “Principles for the effective aggregation of risk data and risk reporting”, was published by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) in 2013 and has been binding for Global Systemically Important Banks (G-SIBs) since 2016. This obliges systemically important banks to implement eleven principles for the effective aggregation of risk data and standardised reporting. In addition, there are three principles for supervisory review – a regulatory foundation for transparency and resilience in the financial sector.
The principles have been binding for G-SIBs since 2016 and have increasingly been applied to Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs) since 2019. The so-called RDARR Framework (Risk Data Aggregation and Risk Reporting) serves the operational implementation of the requirements from BCBS 239 and gives the topic new momentum – especially for D-SIBs and medium-sized institutions.
How does RDARR differ from BCBS 239?
Although RDARR is based on BCBS 239, it goes well beyond the original principles in terms of its practical consequences. The most important developments are
- Auditability and pressure to provide evidence: RDARR is an explicit component of regulatory audits (BaFin §44 KWG, ECB SREP).
- Structured implementation obligation with roadmaps and maturity models
- Technology focus on IT architecture, metadata management, DQ tools
- Interlocking with DORA (e.g. ICT governance, incident reporting)
How can RDARR be implemented in practice? Your 5-step plan for structured implementation
RDARR not only requires new processes, but also a transformation of data management. A proven implementation approach follows these steps:
- Gap analysis and maturity model: evaluation of data flows, responsibilities, IT integration
- Anchoring data governance: introduction of clear roles, steering committees, control inventories
- Measuring and controlling data quality: DQ KPIs, dashboards, control frameworks
- Data lineage and transparency: introduction of tools for data provenance, metadata management
- Dovetailing with DORA and ICT resilience: strategically utilising overlaps.
Why act now? Fit for the audit, fit for the future!
Supervision is becoming increasingly restrictive:
- ECB SREP findings 2023 show incompleteness at many banks.
- BaFin is increasingly using BCBS 239 as an audit standard (Section 44 KWG).
- Pressure for audit readiness including documentation requirements is growing.
Conclusion: RDARR is more than just an update – it is a paradigm shift
RDARR does not require theoretical compliance, but structured, technically implemented data processes with proof of governance. It shifts responsibility to top management and forces operational penetration. Investing now not only avoids audit risks, but also creates the basis for resilient bank management, AI-enabled data infrastructure and regulatory security for the future.
RDARR in practice: Two examples of concrete implementation steps
Example 1: Data quality - from KPIs to institutional management
BCBS 239 ACTUAL status (before RDARR):
The bank has implemented DQ metrics (e.g. completeness, error rate) and provides monthly reports to the data owner. The KPIs are defined in the DWH and are technically measurable.
RDARR requirement:
Supervisors expect data quality to become relevant to management – ie:
- Integration of DQ KPIs into risk reporting and ICAAP reporting
- Concrete measures if limits are exceeded, e.g. escalation to the CRO or data controller
- Audit-proof documentation of corrective measures (Test of Design/ToD, Test of Evidence/ToE)
- Integration of KPIs into an overarching governance framework
Conversion necessary:
- Establishment of a DQ control process (incl. roles, threshold logic, escalation)
- Completion of management reports (e.g. to the Executive Board)
- Adaptation of the control inventory and introduction of a DQ control matrix
Affected processes:
Data management, risk reporting, internal audit, CRO
Duration (realistic):
4-6 months, depending on governance maturity and IT tooling
Example 2: Data lineage - from documented to actively controlled
BCBS 239 ACTUAL status (before RDARR):
The bank has static Excel-based data lineage documentation for key indicators (e.g. LCR, RWA). This is available to the specialist department and the auditor, but is only updated if necessary.
RDARR requirement:
The supervisory authority requires active, audit-proof control and maintenance of the data lineage:
- Systematic maintenance via a central tool
- Connectivity to data catalogue, DQ rules and authorisations
- Traceability of system or model changes (“impact analysis”)
- Integration into the change, release or model control processes
Conversion necessary:
- Introduction or expansion of a data lineage tool
- Connection to source systems (automated scanners if necessary)
- Training of data managers on maintenance and use
- Mapping the lineage in the BCBS 239 reporting framework
Affected processes:
IT architecture, business departments, data management, model validation, IT governance
Duration (realistic):
6-9 months, possibly longer for tool introduction and organisational change
Your implementation partner for RDARR and BCBS 239: Practical. Auditable. Strategic.
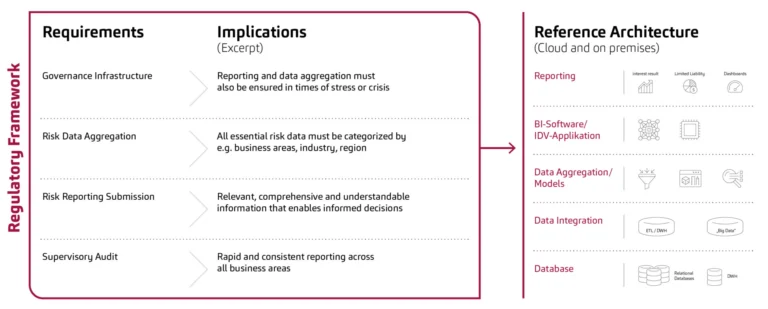
Figure 1: Challenges
Our team provides you with holistic support: from the in-depth gap analysis and maturity assessment to the introduction of governance structures relevant to management through to operational implementation. We deliver robust management reports, provide evidence for BaFin & ECB – and combine your RDARR initiative with regulatory requirements from DORA, MaRisk, BAIT and IT security.
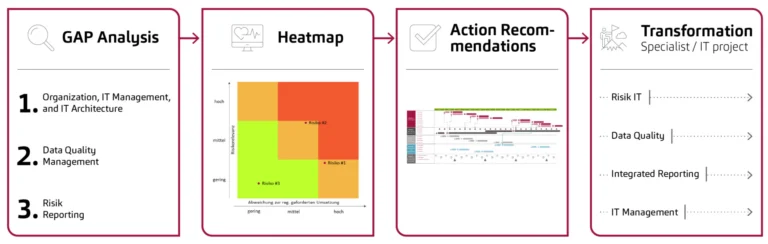
Figure 2: Our support from gap analysis to BCBS239 compliance

Let us examine together where your organization stands and how you can use RDARR as a strategic advantage. Get in touch with our team!










You must login to post a comment.